Related Links
Everything You Need to Know About Radishes

Everything You Need to Know About Radishes

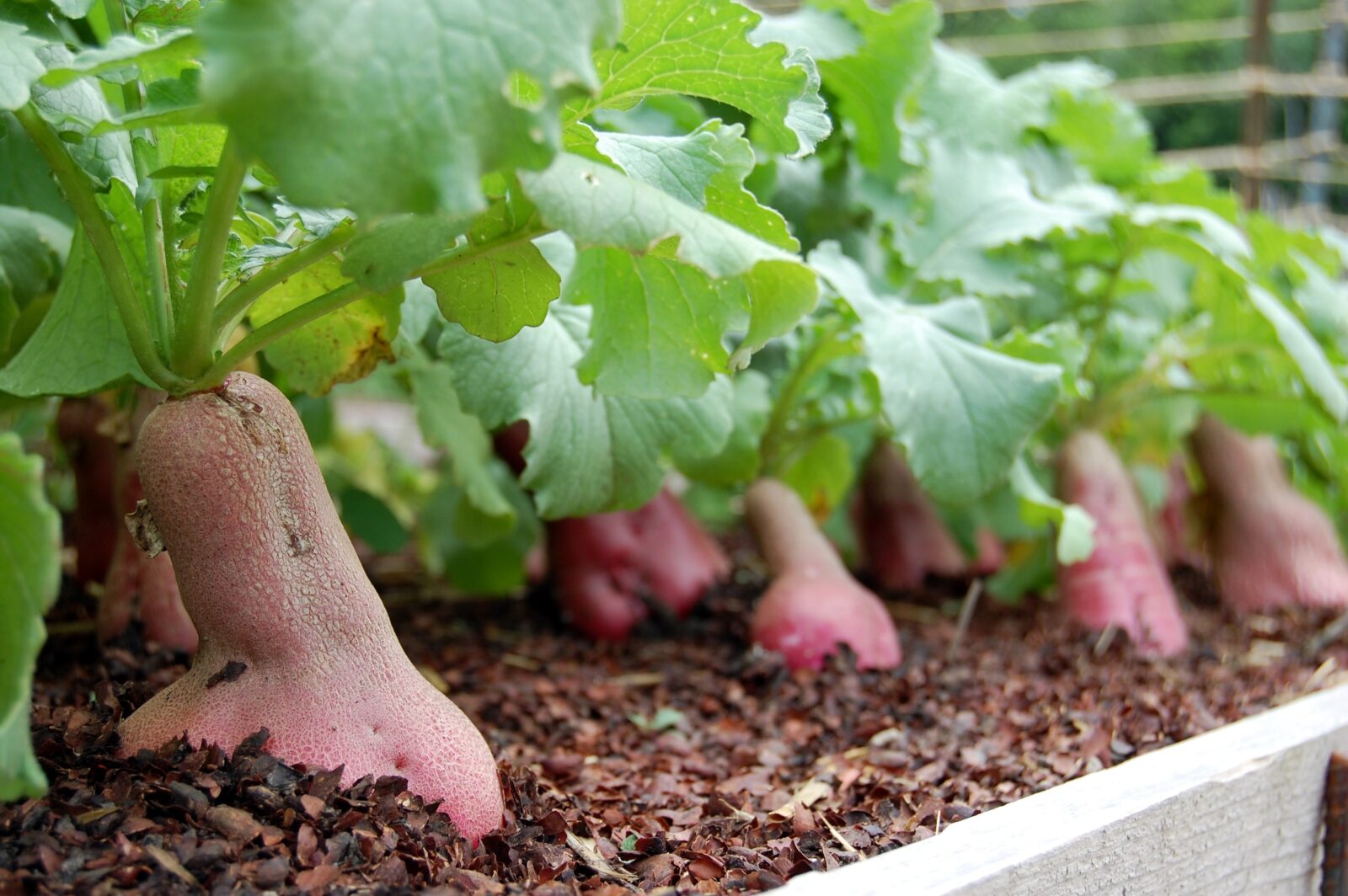
The radishes at Heritage Farm are in full bloom! Our flowering beauties may no longer be edible, but they are well on their way to producing seed. Luckily, most radishes grow quickly and will produce seed in one season.

Cool Radishes
Radishes are wonderfully diverse with many different colors, shapes and sizes! Spring and summer varieties can be pink, red, white, golden, or purple. They can be shaped like bulbs, be more elongated like fingers, or even taper like carrots. Winter varieties are much larger, often black, and need a longer growing season to mature. Daikon radishes, an Oriental winter type, have long white roots prized for their crisp and tender flesh. Some radishes, such as the Rat-Tailed radish, are grown for their edible seed pods rather than their roots. The entire seed pod is edible, and has a lighter radish bite. Who knew?

This season, we grew a very special radish in the Diversity Garden named ‘Colony Summerrettig’. Charles Hoehnle of Homestead, Iowa donated the seed of this variety in 1995. It originated from the Amana Colonies of central Iowa, which were settled in 1856 by a group of German Pietists. These settlers lived a self-sufficient communal life until the mid-1930s. This radish was grown in the colony gardens, prized for its purple roots and ability to reseed for a fall crop. Our planting in the Diversity Garden grew to be quite big before flowering!

How to Grow Radishes
Not only are radishes easy and quick to grow, but you can plant them all season long.
Direct seed radishes 1″ apart and 1/2″ deep as soon as the soil can be worked in the spring. Rows should be 12″ apart for proper root development. When seedlings are about 1″ tall, thin to 2-3″ apart.
Most radishes are ready to eat when their root tops peak out of the soil. Plant successively every 2-3 weeks for a constant supply of radishes.
How to Eat Radishes
Radishes have a spicy bite that makes a wonderful addition to salads and veggie platters. If you’re looking for something different, try sweet and sour radish pickles! Put sliced radishes in a jar with green onions or garlic, and enough vinegar, sugar, and oil to cover. Store in the refrigerator for up to eight hours, making sure to shake the jar every so often. When chilled, you’ll have a tangy treat to enjoy that cuts some of the radish bite but packs a bunch of flavor!
How to Save Radish Seed
Most radish varieties are annuals that will flower and produce seed within one growing season. They are insect-pollinated out-breeders, meaning they will cross with any and all varieties of wild and domesticated varieties. Varieties should be separated by 1/2 mile or more to prevent cross-pollination. If distance or isolation is not possible in your own garden plant a single variety, and be aware if neighboring gardens have different radish varieties flowering at the same time.
Because radishes require that pollen be transferred from one plant to another for successful pollination, a fairly large population size is best for good seed production.
Seed pods will develop on the large flower stalks (up to 3′) and tan as the seed matures and plant begins to dry. Harvest the seed stalks when all parts are fully dry. Seeds are tricky to remove from dried seed pods and may require a bit of force.

This was originally posted on the Seed Savers Exchange blog on June 27, 2012.